The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to 3D Printing: Everything You Need to Know
3D printing has revolutionised the way we create objects, from prototypes to finished products. Whether you’re a hobbyist, an aspiring entrepreneur, or just curious about the technology, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about 3D printing.
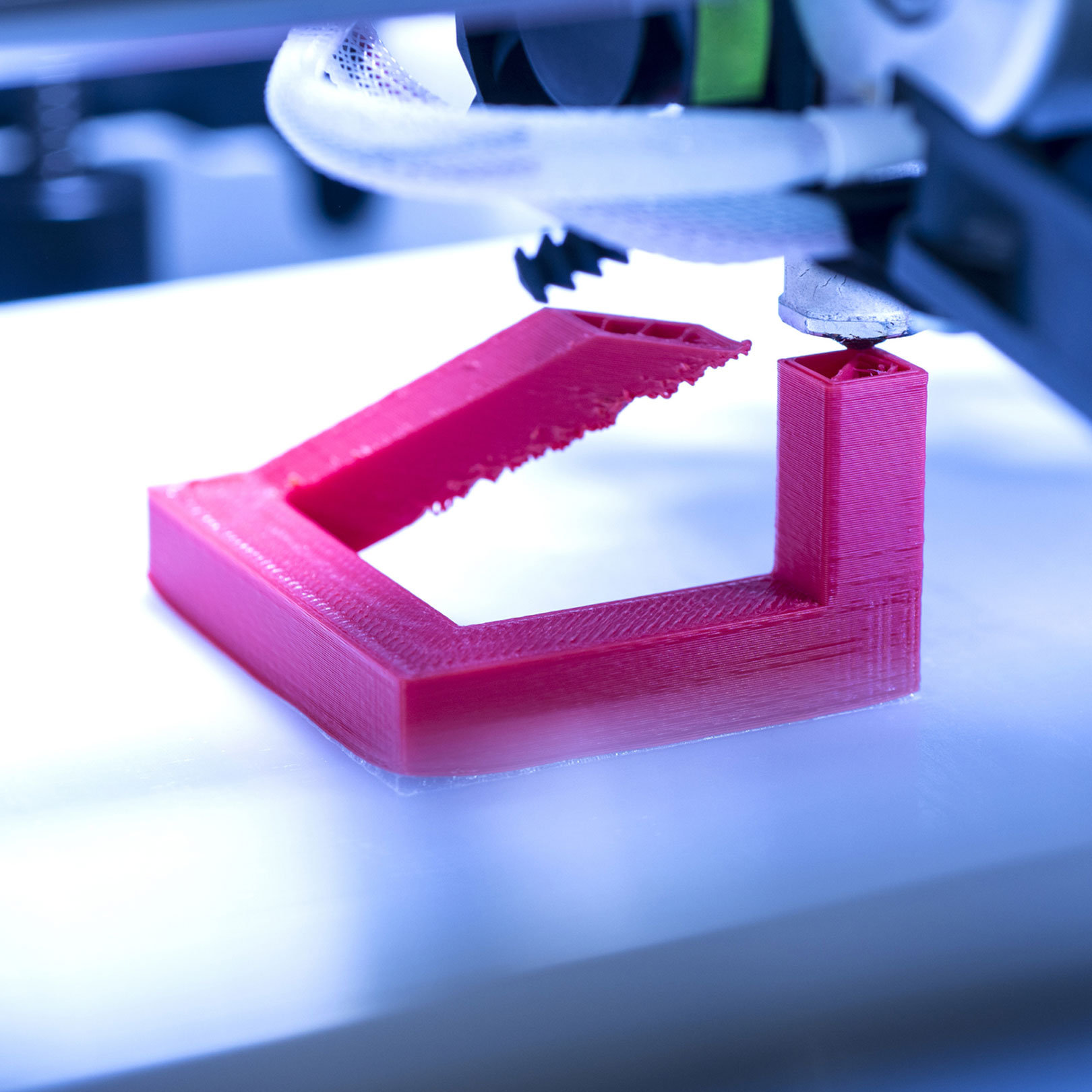
How Does 3D Printing Work?
- Design the Model – Use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software or download pre-made designs from online repositories.
- Prepare the File – Convert the design into a format that the 3D printer can read (typically STL or OBJ files).
- Slicing the Model – Use slicing software to break the model into printable layers.
- Print the Object – The printer deposits material layer by layer until the object is complete.
- Post-Processing – Depending on the material, you may need to sand, paint, or cure the print for a perfect finish.
Types of 3D Printers
There are several types of 3D printers available, each suited to different applications:
-
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) – The most common and affordable type, ideal for beginners.
-
Stereolithography (SLA) – Uses liquid resin and a UV laser to create highly detailed prints.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) – Ideal for industrial applications, using powdered material fused with a laser.
-
Digital Light Processing (DLP) – Similar to SLA but uses a digital light projector instead of a laser.
Best Materials for 3D Printing
The choice of material depends on the application and printer type. Some popular materials include:
-
PLA (Polylactic Acid) – Easy to use, biodegradable, and great for beginners.
-
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) – Strong and durable but requires a heated bed.
-
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) – A balance between PLA and ABS, offering strength and ease of printing.
-
Resin – Used for SLA and DLP printing, offering high detail and smooth finishes.
-
Nylon – Strong and flexible, commonly used in industrial applications.
Essential 3D Printing Software
To start 3D printing, you’ll need the right software:
-
CAD Software – Fusion 360, Tinkercad, or Blender for designing models.
-
Slicing Software – Cura, PrusaSlicer, or Simplify3D to convert models into printable files.
-
Printer Firmware – Ensures your printer operates correctly and efficiently.
Common 3D Printing Issues and How to Fix Them
-
Warping – Ensure the print bed is level and use a heated bed if needed.
-
Layer Shifting – Tighten belts and stabilise the printer’s frame.
-
Poor Adhesion – Use a suitable print surface, such as a PEI sheet or glue stick.
-
Stringing – Adjust retraction settings to minimise excess filament.
Tips for Successful 3D Printing
-
Calibrate Your Printer – Proper calibration ensures accurate prints.
-
Optimise Print Settings – Experiment with temperature, speed, and layer height for best results.
-
Use Support Structures – For overhanging parts, enable supports in your slicer.
-
Maintain Your Printer – Regularly clean nozzles, check belts, and update firmware.
Future of 3D Printing
3D printing is continuously evolving, with new materials, faster printing speeds, and applications in industries like healthcare, aerospace, and fashion. As technology advances, 3D printing will become more accessible and versatile than ever before.
Conclusion
Getting started with 3D printing may seem daunting, but with the right knowledge, anyone can create amazing objects from digital designs. Whether you’re printing for fun, education, or business, this exciting technology offers limitless possibilities.
Ready to Start 3D Printing?
Explore beginner-friendly 3D printers, download free models, and join online communities to learn and share your creations!
